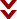
The International Hotel struggle and the Filipino community
August 4, 1977 will go down in infamy as the date the City and County of San Francisco executed the most ruthless persecution and violent destruction of human life unparalleled ever except for the 1934 General Strike. The main blow was directed at Manilatown and the Filipinos who lived on Kearny Street since the early 1900's.
Final evictions were carried out in 1977. For those elderly Filipinos and Chinese who fought and stood in defense of their home that night, it was a sad commentary of how inhumane their treatment and the disgrace of a city uncaring to handle the housing crisis and the homeless victims of this and other evictions. However, continued community organizing prevented the owner from building his planned development, even after the building was demolished in 1981. The hole in the ground served for years as a glaring reminder of the human costs and sacrifices to defend affordable housing for minorities and the poor.
In 1994 the owner agreed to sell the property to the Catholic diocese, leading to the construction of a new I-Hotel of low-cost senior housing with a Filipino community center which opened in 2005.